Google Adds Custom Chart Annotations to Search Console — A Game-Changer for SEO Tracking

Google has officially rolled out Custom Chart Annotations inside the Search Console Performance reports, giving SEO professionals the ability to add their own contextual notes directly on performance charts.
This feature was launched globally on November 17, 2025, and is one of the most requested enhancements since Search Console’s redesign in 2018.
Think of it as a personal SEO notebook built into your analytics dashboard — helping you mark when important website or SEO changes occurred.
🗓️ What Are Custom Annotations in Google Search Console?
Annotations in Search Console provide context for performance data by letting you tag events directly on charts. Google has introduced two types of annotations:
- System annotations — Added automatically by Google to show issues with data processing or known reporting changes.
- Custom annotations — Created manually by users to mark important events like site migrations, algorithm updates, or SEO strategy changes.
Once added, annotations appear as small markers on the chart, visible to all verified users who have access to the property.
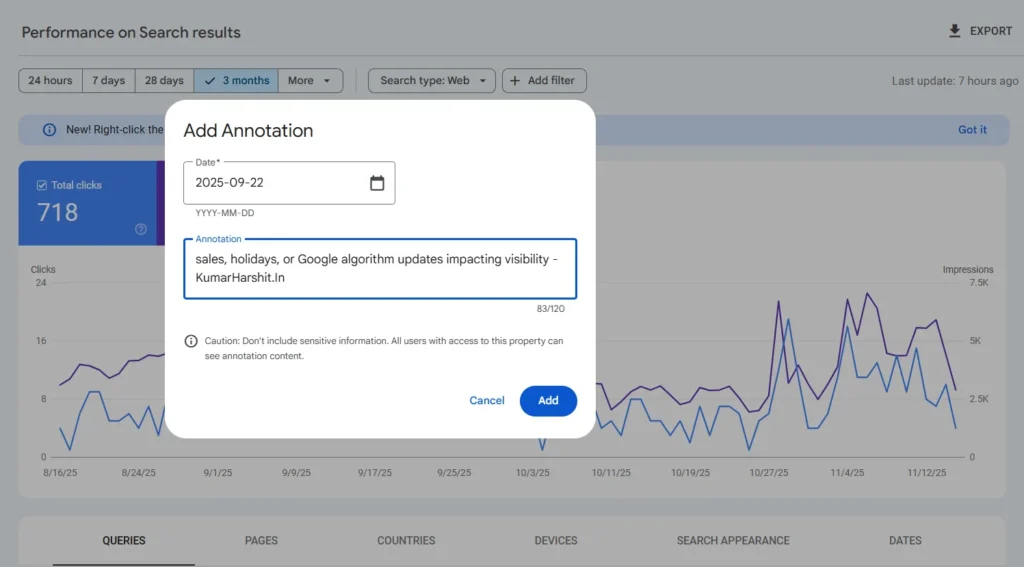
⚙️ How to Add, View, or Delete Custom Annotations
You can create and manage up to 200 annotations per property.
Step-by-Step:
- Open your property in Search Console.
- Go to the Performance report (Search Results, Discover, or News).
- Right-click on a specific date in the chart where you want to add the note.
- A pop-up window titled “Add Annotation” will appear.
- Enter a short note (up to 120 characters).
- Click Add to save it.
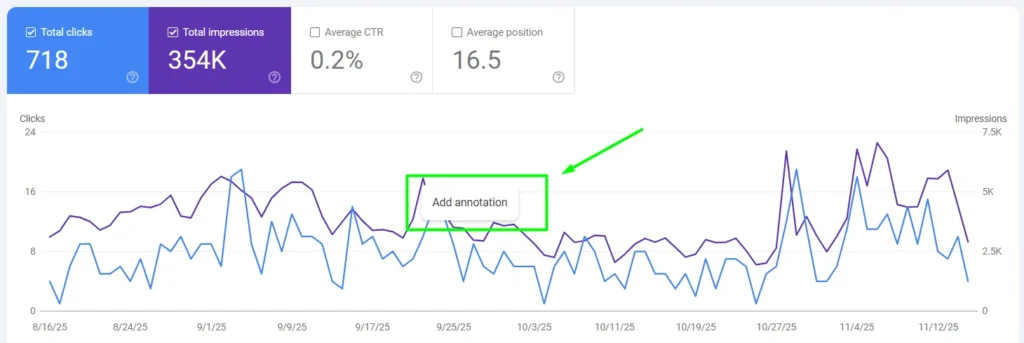
You can also delete annotations by clicking on the marker and selecting Delete.
🔒 Privacy Note:
Annotations are shared across all property users and should not contain personal or sensitive data such as names, phone numbers, or internal business details.
(Official guideline: Google Search Console Help — Annotations)
🧠 Best Use Cases for Custom Annotations
Google suggests using annotations to track key milestones or SEO-related changes that could affect performance metrics.
Some examples include:
- 🔧 Website infrastructure updates — e.g., site migrations, redesigns, or hosting changes.
- 🧩 Plugin or tracking changes — installing analytics scripts, schema updates, or CMS plugin modifications.
- 💼 Marketing campaigns — recording start or end dates of paid or organic campaigns.
- 📈 SEO strategy shifts — focusing on new intent clusters or keyword segments.
- 📅 External events — sales, holidays, or Google algorithm updates impacting visibility.
This helps SEOs easily correlate ranking or traffic fluctuations with specific site or strategy changes.
💡 Why It’s a Game-Changer for SEOs and Web Analysts
Before this update, tracking context behind performance data required external notes or using Google Sheets or third-party tools.
Now, annotations are natively integrated into Search Console — ensuring all data and insights stay in one place.
Key Benefits for SEOs:
- 🕓 Saves time: No need to maintain external logs.
- 📊 Data transparency: All verified users see the same annotation markers.
- 📈 Faster insights: Makes it easier to identify when ranking or traffic changes started.
- 💬 Team collaboration: Multiple users on the same property can view and coordinate around shared events.
- 🔍 Better reporting: Adds qualitative context to quantitative data, improving SEO audits and month-over-month reports.
🧩 System vs Custom Annotations — The Difference
| Type | Who Adds It | Purpose | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| System Annotation | Automatically logs issues with data processing or Search Console reports | “Data anomaly on Nov 5 — indexing issue resolved” | |
| Custom Annotation | You | Tracks internal SEO or site events | “Added new XML sitemap” or “Deployed core web vitals fix” |
📈 SEO Industry Impact
This release is especially useful for agencies, in-house SEO teams, and consultants who manage multiple websites.
It introduces a built-in mechanism for correlating technical, content, or algorithmic changes with Search performance — something long missing from native GSC tools.
For AI-driven SEO workflows, annotations can also act as event labels when exporting Search Console API data — making machine learning analysis of ranking trends more context-aware.
🚀 Final Thoughts
With this update, Google continues improving Search Console as an SEO intelligence platform, not just a reporting dashboard.
By adding annotation tracking, Google empowers SEOs to make data-driven decisions faster and maintain better visibility across every optimization step.
This update is rolling out globally — so if you don’t see the “Add Annotation” option yet, check again over the coming days.
FAQ
It was officially launched on November 17, 2025, as announced on the Google Search Central Blog.
Go to Search Console → Performance Report, right-click a date on the chart, and select “Add Annotation.”
All verified property users can see custom annotations. However, only full-access users can create or delete them.
No. Annotations older than 500 days are automatically deleted by Google.
Avoid entering personal or confidential information — annotations are visible to everyone with property access.
Author
Harshit Kumar is an AI SEO Specialist with 7 + years of experience in SEO automation, Google Search updates, and structured data optimization. He helps marketers stay ahead of every major search algorithm and seo tool change.


Leave a Reply