Can ChatGPT Catch Google? A Data-First Look at Scale, Speed, and the Realistic Timelines
When people compare Google and ChatGPT they often reach for a single question: “Which one has more daily searches?” That’s the wrong question — but it’s an understandable start. The better question is: how do the two platforms differ in scale, intent, and growth velocity — and what do those differences imply for the future of search and discovery? Those implications increasingly matter for brands, which now need visibility not just in Google rankings but inside AI-generated answers, a shift driving the rise of AI visibility platforms like Wellows, an autonomous marketing platform for GenAI that tracks brand mentions, citation presence, and real visibility across AI systems.
This article walks through the real, public numbers, explains exactly what each metric means, and shows why ChatGPT’s speed of adoption is the real story — even if raw, apples-to-apples parity still looks far off today.
The headline numbers you need to know (and what they actually measure)
First — the raw counts that get quoted in headlines:
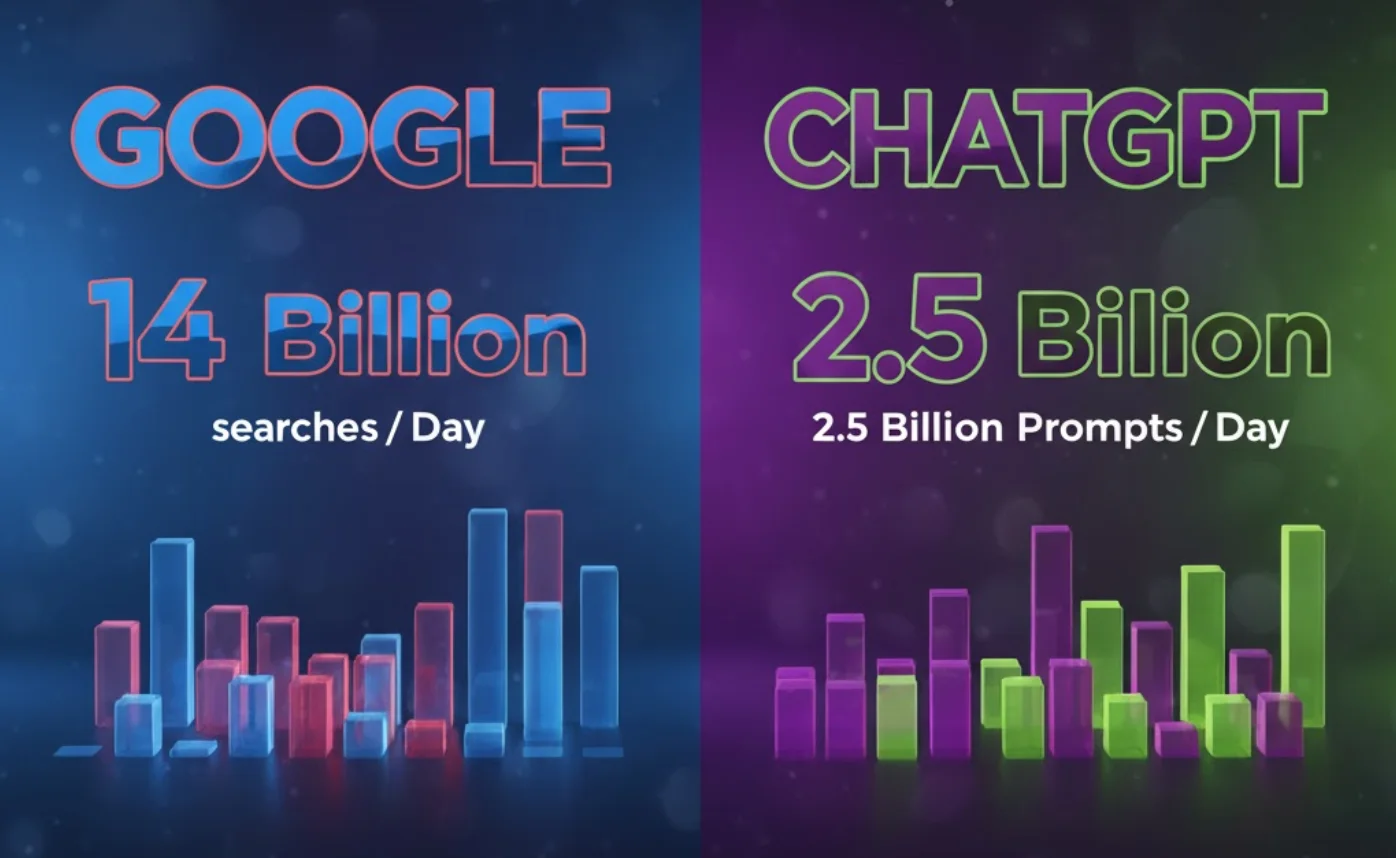
- Google: roughly 14 billion searches per day (≈5+ trillion per year). This is the canonical “searches/day” figure used across industry reporting.
- ChatGPT (all prompts/messages): OpenAI has reported that users send ~2.5 billion prompts (messages) per day to ChatGPT — that is, all interactions that invoke the model. (Source: TechCrunch)
- ChatGPT (search-like prompts): When researchers and analysts filter ChatGPT conversations for those that look like traditional keyword searches (a closer apples-to-apples comparison), the commonly cited figure is ~66 million search-like prompts per day. That’s the metric analysts use when they want to compare ChatGPT directly with Google’s classic search queries.
Crucial distinction: “prompt” or “message” ≠ “search”. ChatGPT conversations are multi-message, conversational sessions; a single user session can generate many messages. Analysts therefore create a “search-like” subset to compare to Google’s query counts. Keep that in mind when reading ratios below.
Apples → Apples? Why direct comparisons are misleading unless you define the metric
Think of Google as a decades-old infrastructure that optimized for keyword queries, page indexing, and link-based relevance. Its core metric — search queries — counts discrete keyword hits. ChatGPT, by contrast, measures interactions with a conversational model: prompts, follow-ups, clarifying messages, multi-step sessions, and automation calls.
So there are two valid comparison modes:
- Raw model interactions (broad engagement): 2.5B ChatGPT prompts/day vs. 14B Google searches/day. This shows ChatGPT is already operating at multi-billion scale — remarkable for a product born in late 2022. (Source: TechCrunch)
- Search-like intent only (narrowed comparison): ~66M ChatGPT search-like prompts/day vs. 14B Google searches/day. This isolates the subset of ChatGPT usage that most closely resembles classic search behavior. Under this lens, Google still dwarfs ChatGPT in search-style queries.
Both are useful. If your headline is “which platform handles more search-style queries?” use the 66M vs 14B comparison. If your question is “which platform processes more total user interactions that can deliver answers and automate tasks?” use the 2.5B vs 14B comparison.
How big is the gap — exact numbers and ratios
Let’s put the two comparisons into concrete ratios (calculated precisely):
- Using total prompts: 2.5 billion (ChatGPT) ÷ 14 billion (Google) ≈ 0.1786 → ChatGPT is roughly 5.6× smaller than Google in raw interactions (i.e., Google ≈ 5.6× the raw daily interaction volume). (Source: TechCrunch+1
- Using search-like prompts: 66 million (ChatGPT search-like) ÷ 14 billion (Google) ≈ 0.0047 → Google is about 212× larger than ChatGPT on pure, search-style queries. (14,000M ÷ 66M ≈ 212.12).
Important takeaways from those ratios:
- By total message volume ChatGPT already operates at a multi-billion daily scale — small but not tiny relative to Google.
- By search-style queries, Google still dominates by two orders of magnitude.
The real variable: adoption speed — ChatGPT’s historic advantage
Raw size today is only part of the picture. Growth rate — how fast usage increases — determines who closes gaps.
- Google’s ascent to multi-trillion annual searches came gradually over nearly two decades, aided by browser defaults, OEM partnerships, and SEO-driven web growth.
- ChatGPT launched publicly in late 2022 and in ≈2–3 years reached hundreds of millions of weekly users and billions of daily prompts. OpenAI’s economic research and public statements document this rapid diffusion: hundreds of millions of users and ~2.5B prompts/day — an adoption curve with virtually no precedent in consumer software. ( Source: OpenAI)
Why so fast? A few structural reasons:
- Viral shareability: One impressive ChatGPT answer is easy to screenshot and share, which accelerates discovery in ways search results rarely do.
- Developer and enterprise integrations: APIs, plugins, and embedded assistants multiply touchpoints beyond a standalone app.
- Task value beyond retrieval: ChatGPT performs synthesis, draft writing, code assistance, and automation — use cases that create stickier, more frequent interactions than single keyword lookups. (source: OpenAI)
If current trends continue: scenario sketches for “parity”
“Parity” depends on definition. Here we demonstrate search-style parity (ChatGPT’s search-like prompts reach Google’s 14B/day). These are illustrative, not predictions.
Start baseline: 66M search-like prompts/day.
- Slow-growth scenario (flat adoption): If ChatGPT’s search-like prompts remain near 66M/day, no parity — Google remains dominant indefinitely for this kind of query.
- Moderate-growth scenario (×3 year-over-year for search-like prompts):
Year 1: 66M ×3 = 198M/day
Year 2: 198M ×3 = 594M/day
Year 3: 594M ×3 = 1.78B/day
Year 4: 1.78B ×3 = 5.34B/day
Year 5: 5.34B ×3 = 16.0B/day → parity in ~5 years.
This assumes product improvements, integrations, and user intent migration continue strongly. - Fast-growth scenario (×4 year-over-year):
Year 1: 66M ×4 = 264M/day
Year 2: 264M ×4 = 1.06B/day
Year 3: 1.06B ×4 = 4.24B/day
Year 4: 4.24B ×4 = 16.96B/day → parity in ~4 years.
Note: if you use the broader base (2.5B total prompts/day), timelines become much shorter for parity measured on raw interactions — but those interactions are not all search-style and so may not map to the same business/advertising ecosystem as Google Search.
Structural advantages that can accelerate ChatGPT’s climb
- Integrations across products and workflows. When ChatGPT is embedded in email, docs, browsers, and enterprise software, every app becomes a new acquisition channel — multiplication by distribution partnerships. (Source: OpenAI)
- One remarkable answer = instant PR/virality. Human-sharing is a powerful growth engine for generative AI outputs.
- Automation & agent-style features. As models act on behalf of users (bookings, code edits, summarization), usage frequency rises beyond simple queries. (Source: OpenAI)
The headwinds that will slow or reshape parity
- Different intents and UX expectations. People still rely on search engines for maps, local results, shopping price comparisons, and long-tail discovery — features Google has deeply optimized. ChatGPT will need to replicate or integrate those capabilities meaningfully to supplant many queries.
- Ads & monetization. Google’s ad ecosystem funds its index, infrastructure, and billions in product investment. Displacing that business model requires mature monetization options for AI assistants.
- Accuracy, hallucinations, and trust. Generative models can fabricate plausible but incorrect facts. Large-scale migration away from a verifiable index to model-generated answers will depend on improved guardrails and fact-checking systems. (Source: OpenAI)
- Regulation & geopolitical pressure. AI at scale attracts policy scrutiny that could limit features and cross-border deployments. (Source: Reuters)
What parity would actually imply (for users, publishers, and advertisers)
If ChatGPT reaches parity on search-style queries it would mean:
- A meaningful fraction of discovery queries move from ranked web pages to model-synthesized answers. That changes referral traffic patterns for publishers.
- Advertisers must rethink placements — conversational ads? sponsored answers? new APIs for intent monetization.
- SEO evolves: optimizing for model knowledge retrieval and structured data that models trust could become as important as classic ranking signals.
But parity on raw interactions (2.5B → 14B-style counts) would be a different play: more automation, more “assistant” use, but not necessarily an immediate swap of ad monetization mechanics.
Conclusion
- Today: Google still processes far more traditional search queries (≈14B/day) than ChatGPT’s search-like prompts (≈66M/day). But ChatGPT already handles billions of total prompts per day (≈2.5B), which is an extraordinary scale for a tool born in 2022.
- Why it matters: The speed of ChatGPT’s adoption — hundreds of millions of users and multi-billion daily interactions inside a few years — is the competitive force that could compress many decades of incumbency advantage into a far shorter timeline.
- Realistic parity: For ChatGPT to match Google on search-style query volume, aggressive but plausible growth could deliver parity in 3–6 years under positive scenarios. However, parity in advertising dollars, index depth, and local/shopping intents is a different (and harder) problem.
✍️ About the Author
Harshit Kumar is an AI SEO Specialist and founder of KumarHarshit.in — a platform known for building innovative SEO automation tools like the AI Internal Linking Plugin and Free News Sitemap Generator.
With deep expertise in AI-driven SEO and content automation, Harshit focuses on bridging the gap between traditional search optimization and the future of conversational AI.
He regularly shares insights on how AI models like ChatGPT are reshaping search behavior, SEO strategies, and content discovery across the web.
Follow Harshit on LinkedIn for data-backed discussions, real experiments, and future-focused SEO research.


Leave a Reply