Yoast SEO llms.txt Feature: Full Technical Guide, Setup, Use Cases & Best Practices

Modern SEO is rapidly evolving beyond search engines. Today, content is being indexed not only by Google and Bing but also by AI systems like ChatGPT, Google Gemini, Perplexity, Claude, and other generative search tools. As AI-driven search becomes mainstream, correct indexing signals and content access instructions are becoming increasingly important for website owners—especially those running education-focused or gated content platforms.
To support this shift, Yoast SEO introduced a new feature called llms.txt. While many website owners have seen this option in their settings, most are unaware of what it does, whether they need it, and when it should be configured.
This guide provides a complete, technical, and professional breakdown of the llms.txt file in Yoast SEO, how it affects indexing behavior, setup steps, configuration examples, and best practices to determine whether your website should enable it.
What Is the llms.txt File?
The llms.txt file is a newly introduced structured configuration file in Yoast SEO designed to help AI crawlers—especially Large Language Model systems (LLMs)—understand how your learning-based or gated content website is structured.
Unlike robots.txt, which primarily controls crawling behavior for traditional search engines, llms.txt serves as a metadata and indexing signal specifically for AI tools. Its purpose is to clarify which parts of a website contain structured course content, restricted learning materials, lessons, progress-tracking pages, or student-only access segments.
Simple Definition
The llms.txt file allows a website owner to inform AI crawlers about course-related or learning-specific content, while optionally restricting private learning modules, quizzes, and member-only material from being indexed or used as AI training data.
Why Does This Matter?
Many learning platforms (course portals, tutorials, paid webinars, and membership systems) contain a mix of:
- Public landing pages
- Module pages
- Lesson content
- Quiz structures
- Logged-in student-only content
- Certificates and progress tracking URLs
Traditional search engines struggle to crawl these cleanly, and AI crawlers risk accessing or using restricted content.
The llms.txt file solves this problem by:
- Marking structured learning content
- Protecting private material
- Providing context signals for content categorization
- Improving AI and search engine understanding of content structure
Example of What an llms.txt File Might Contain
(This is a conceptual placeholder example)
# Accessible learning content
Allow: /course/introduction/
Allow: /course/module-1-overview/
# Restricted student-only content
Disallow: /course/module-2/lesson-1/
Disallow: /course/module-2/quiz/
Why Yoast Introduced This Feature
The introduction of llms.txt aligns with three major shifts in modern search and content discovery:
✔ Shift #1 — AI-Based Indexing and Content Understanding
AI systems differentiate between:
- Public content meant to be indexed and referenced
- Protected content not meant for modeling or aggregation
The llms.txt file helps communicate this distinction.
✔ Shift #2 — Growing Adoption of LMS Websites
More websites now host:
- Online courses
- Private coaching areas
- Members-only knowledge bases
- Tutorials behind paywalls
Such structures require granular content access control—something robots.txt cannot fully define.
✔ Shift #3 — Copyright, Licensing, and Content Usage Rights
Content owners need a method to:
- Inform AI not to use certain content for training
- Declare intellectual property restrictions
- Define content visibility scope
llms.txt provides that compliance layer.
How the llms.txt File Works (Technical Breakdown)
The llms.txt file functions as a machine-readable instruction layer for AI systems and next-generation indexing tools. While humans rarely need to access it directly, AI crawlers interpret it to understand:
- Which pages belong to structured learning content
- Which content is public vs. restricted
- How accessibility rules apply to course elements
- Whether the content is permitted for AI training, display, or summarization
Unlike standard SEO files used today, llms.txt is not primarily about ranking. Instead, it focuses on content categorization, access clarity, and compliance for content consumption by AI agents.
Key Concepts the File Communicates
| Instruction Type | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Content categorization | Helps AI classify lessons, modules, quizzes, or gated educational pages. |
| Access permissions | Defines public vs private content accessibility. |
| Training usage permissions | Advises whether AI tools may use content for dataset training or retrieval. |
| Structured learning signals | Identifies format patterns such as sequential lessons or modules. |
How AI Systems Use This File
LLMs use llms.txt for:
- Detecting whether content can be summarized
- Identifying if content is part of a learning sequence
- Avoiding legally-protected or subscription-based material
- Preventing hallucinations caused by misinterpreting gated content
This file acts like a policy rulebook for content usage transparency.
llms.txt vs robots.txt vs sitemap.xml
It’s common for website owners to confuse llms.txt with other indexing-related files. While they share similarities, each serves a unique purpose.
Comparison Table
| File Type | Who Reads It | Primary Purpose | Content Access Role |
|---|---|---|---|
| robots.txt | Traditional search crawlers (Googlebot, Bingbot) | Control crawling & indexing | “Should the bot crawl this content?” |
| sitemap.xml | Search engines | Provide structured list of URLs | “Here is what exists and should be indexed.” |
| llms.txt | AI crawlers & LLM indexing tools | Declare learning content & access level | “How should this content be interpreted and used?” |
Where Each File Fits in an Indexing Workflow
Site → robots.txt → sitemap.xml → llms.txt → Content access interpretation
In this flow:
- robots.txt controls crawling permission
- sitemap.xml declares available URLs
- llms.txt explains how learning content should be treated
Example Flow In Practice
If a URL is:
- Allowed in
robots.txt - Listed in
sitemap.xml - But marked restricted in
llms.txt
→ AI crawlers may crawl the page, but not store, reuse, or train from it.
This makes llms.txt especially valuable for ownership-protected learning content.
When You Should Enable This Feature
The llms.txt feature is useful on websites containing structured learning experiences, including:
- Online courses
- Coaching or workshop modules
- Subscription learning areas
- Lesson series with progress tracking
- Premium content libraries
- Digital academies
- Tutorial series requiring login
Ideal Situations to Enable
✔ You have a gated lesson structure
✔ Your website contains premium or copyrighted material
✔ AI tools should access only limited or preview-level content
✔ You want AI systems to correctly classify course content
✔ Your site uses:
- LMS plugins
- Membership plugins
- Learning modules
- Lesson pipelines
When enabled in such environments, llms.txt improves both content protection and structured understanding.
When You Should NOT Enable It
This feature is not necessary for websites without learning-based structuring.
You should not enable the llms.txt option if your site is:
| Site Type | Should You Enable? |
|---|---|
| Blog | ❌ No |
| Personal brand portfolio | ❌ No |
| E-commerce | ❌ No |
| Standard service website | ❌ No |
| Business homepage | ❌ No |
| News, review, or informational site | ❌ No |
Enabling it unnecessarily may:
- Create irrelevant indexing rules
- Confuse AI systems
- Signal false course structure
- Limit AI exposure of content that should remain public
Simple Rule
Enable llms.txt only if your website contains structured, gated, or curriculum-based learning content.
How to Enable and Configure llms.txt in Yoast SEO
The llms.txt feature is located inside the Yoast SEO Advanced Settings panel. Website owners can choose between two configuration modes:
- Automatic page selection
- Manual page selection
This ensures flexibility depending on whether the learning content is automatically generated or uniquely structured.
Below is a complete setup guide.
Step-by-Step Setup Guide
Step 1 — Access the llms.txt Feature
- Log in to WordPress admin.
- Navigate to:
Yoast SEO → Settings → Advanced → llms.txt
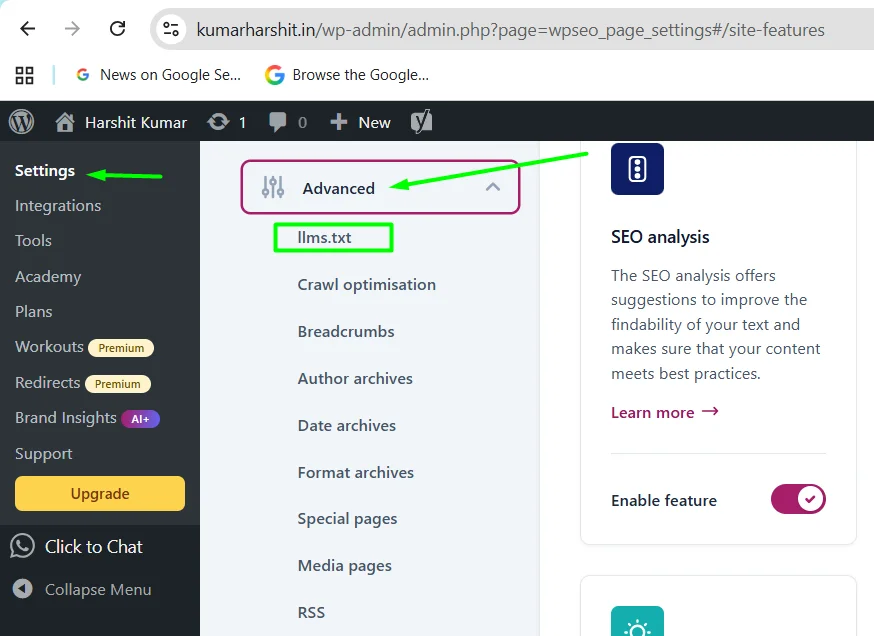
Step 2 — Enable the Feature
Toggle the switch:
Enable llms.txt file → ON
Once enabled, Yoast will generate the file and make it available for AI crawlers.
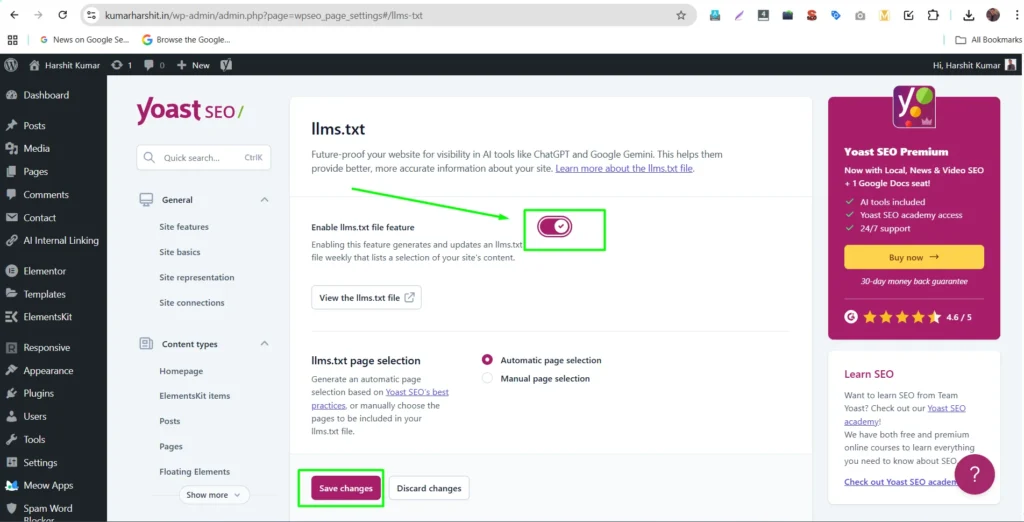
Step 3 — Select Configuration Mode
You now select how Yoast will populate the llms.txt structure:
| Option | Best For | Configuration Difficulty |
|---|---|---|
| Automatic Page Selection | Standard LMS sites using common course structures | ⭐ Easy |
| Manual Page Selection | Custom content architecture, hybrid gated models | ⭐⭐⭐ Advanced |
Automatic Page Selection (Recommended for LMS Websites)
When you select this mode, Yoast will attempt to:
- Detect lesson templates
- Identify module structures
- Determine login-only content
- Classify gated pages into allow/disallow groups
Yoast uses its internal rules and LMS pattern detection logic to create a structured llms.txt configuration automatically.
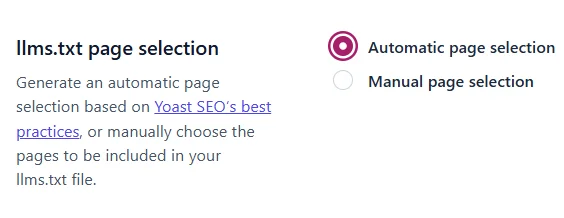
Manual Page Selection (Advanced Mode)
If a site has a unique learning flow, membership logic, or mixed structure, this mode allows full control.
You can manually choose:
- Which categories define public learning content
- Which pages represent restricted access
- Which URLs should be:
- Allowed
- Disallowed
- Partially visible
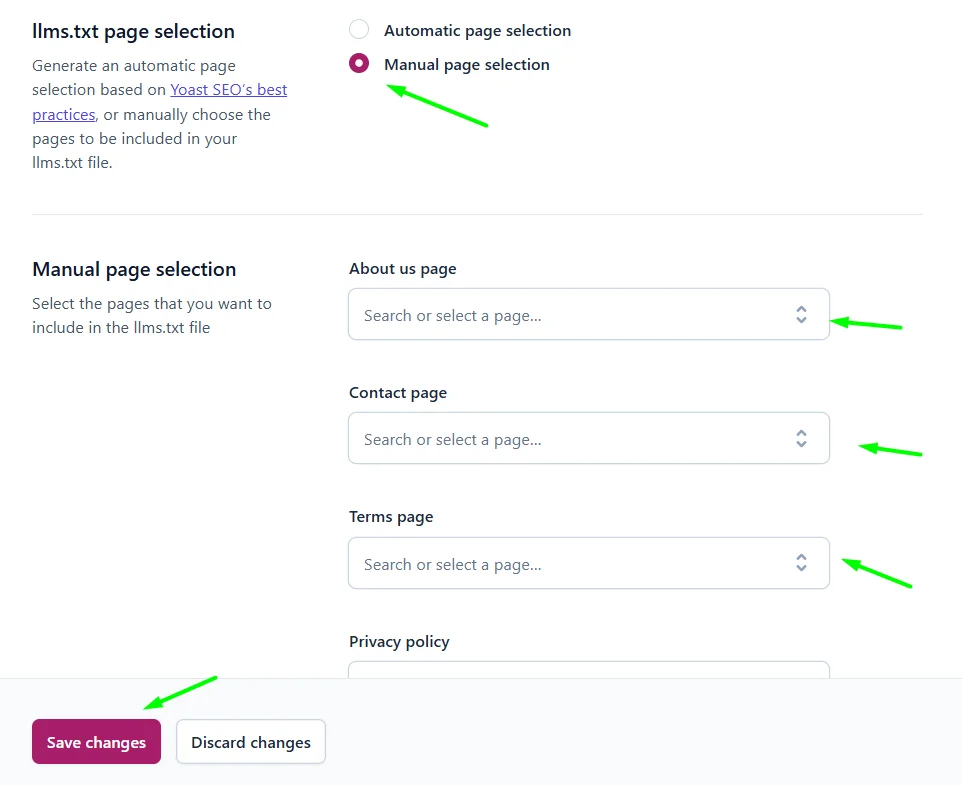
Fields Available in Manual Mode
| Field Name | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Contact page | Defines non-learning but essential access pages |
| Privacy policy | Clarifies content use rules for AI |
| Terms page | Used to ensure AI understands licensing |
| Shop page | Only applicable if selling course materials |
| Content pages | Used to define gated learning modules |
Each entry becomes a rule in the llms.txt file.
How to View Your Generated File
After configuration, select:
View the llms.txt file
This opens a preview similar to:
# llms.txt generated by Yoast SEO
Allow: /course/intro/
Disallow: /course/module-3/lesson-2/
Disallow: /course/module-3/exam/Recommended Best Practices
To ensure correct usage and avoid accidental access restrictions, follow these best practices:
✔ Keep the Structure Simple
Use consistent URL patterns for learning pages, such as:
/learn/
/course-name/module-01/
/lesson-name/
Avoid:
/random-page-1/?lesson=4567&preview
✔ Test File Visibility
The final file must load publicly:
https://yourwebsite.com/llms.txt
If the file returns:
- Redirect loops
- 404 errors
- Authentication prompts
→ Review caching and firewall rules.
✔ Align with robots.txt and Sitemap
Ensure no conflicting instructions exist.
Example conflict to avoid:
robots.txt: Allow /course/module-1/
llms.txt: Disallow /course/module-1/
This creates mixed signals and may reduce crawler efficiency.
✔ Update the File When Adding New Courses
Whenever new:
- Lessons
- Modules
- Restricted member content
are added, verify llms.txt remains accurate.
Pros and Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Protects gated learning content | Not needed for non-learning websites |
| Helps AI categorize structured courses | Incomplete configuration can cause indexing confusion |
| Supports licensing clarity and compliance | Requires maintenance for expanding course libraries |
| Future-proofing against AI-driven search | Limited immediate visible SEO ranking benefit |
Checklist Before Enabling
Use this validation flow:
| Question | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|
| Does my site contain courses or structured learning content? | ☐ | ☐ |
| Do some pages require login access? | ☐ | ☐ |
| Does the content need partial visibility to AI? | ☐ | ☐ |
| Do I want to restrict AI from using certain content for training? | ☐ | ☐ |
➡ If majority are YES → Enable.
➡ If mostly NO → Leave disabled.
Example Scenarios (Using Neutral Non-Branded Use Cases)
To better understand how llms.txt applies in real-world environments, here are structured example scenarios without referencing any specific external domain.
Scenario 1 — A Public Course With Free Lessons and Premium Modules
A website publishes an introductory course freely available but locks advanced modules behind login access.
- The free lessons should be discoverable by AI and search engines.
- The advanced content should remain behind a paywall.
Suggested llms.txt Rules:
Allow: /course/fundamentals/
Allow: /course/module-1/lesson-1/
Disallow: /course/module-2/
Disallow: /course/module-3/
Disallow: /course/exams/
Outcome:
- AI systems can reference public lessons.
- Restricted content remains protected.
Scenario 2 — A Membership Site With Tutorials and Downloads
Some pages may contain written guidance intended for wider discovery, while downloadable materials (PDFs, worksheets) are exclusive to paid members.
Allow: /learn/tutorials/
Disallow: /learn/download-center/
Disallow: /learn/member-files/
Outcome:
- Tutorials become categorized as educational content.
- Member-only assets remain inaccessible.
Scenario 3 — Private Employee Training or Internal Education System
If a company uses WordPress as an internal learning hub, all content should remain restricted from indexing.
Disallow: /
Outcome:
- AI crawlers receive a blanket restriction.
- No educational content is classified or reused.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
No — this file does not directly affect search rankings.
Its purpose is content classification and access signaling for AI systems—not ranking algorithms.
Traditional search crawlers like Googlebot and Bingbot may detect the file, but currently, it is mainly intended for AI crawlers and future indexing systems.
Only when the option is enabled. The content may be automatic or manual depending on which mode you select.
Yes — but only if your site contains content structured like lessons or gated learning modules. Otherwise, enabling it offers no benefit.
It signals intent, but compliance depends on how AI companies adhere to the protocol. The file acts as a governance indicator, not a guaranteed enforcement tool.
Currently, editing happens inside Yoast settings—not via file manager. Yoast controls the generation logic.
No — it works alongside them and does not replace either file.
Conclusion
The llms.txt feature introduced by Yoast SEO represents an important step toward preparing websites for the next era of search—where AI systems and learning-based indexing models play a central role in content discovery.
For websites using structured learning content such as courses, modules, and gated educational material, this feature provides:
- Better clarity for AI indexing
- Permission controls for training data usage
- Structured content categorization
- Additional protection for premium content
However, for standard websites without educational content or lesson-based architecture, enabling this feature offers no operational or SEO advantage—and may create unnecessary indexing complexity.
To determine whether to activate this feature on your website, simply ask:
“Does my website contain structured educational content that needs controlled access?”
If yes, enabling and configuring llms.txt is a smart forward-thinking move.
If not, it is best left disabled.
Final Takeaway:
llms.txt is not a ranking tool — it is a visibility, protection, and compliance tool for learning-based content in an AI-indexed future.
Author
Harshit Kumar is an AI SEO Specialist and the founder of kumarharshit.in. With 7+ years of experience in technical SEO, AI search adaptation, and advanced indexing strategies, he helps businesses future-proof their visibility across traditional search engines and emerging AI-driven discovery platforms. His work focuses on building scalable SEO systems, content frameworks, and practical implementation guides for website owners and digital professionals.


Nice blog here Also your site loads up fast What host are you using Can I get your affiliate link to your host I wish my web site loaded up as quickly as yours lol
https://hostinger.in?REFERRALCODE=1HARSHIT459